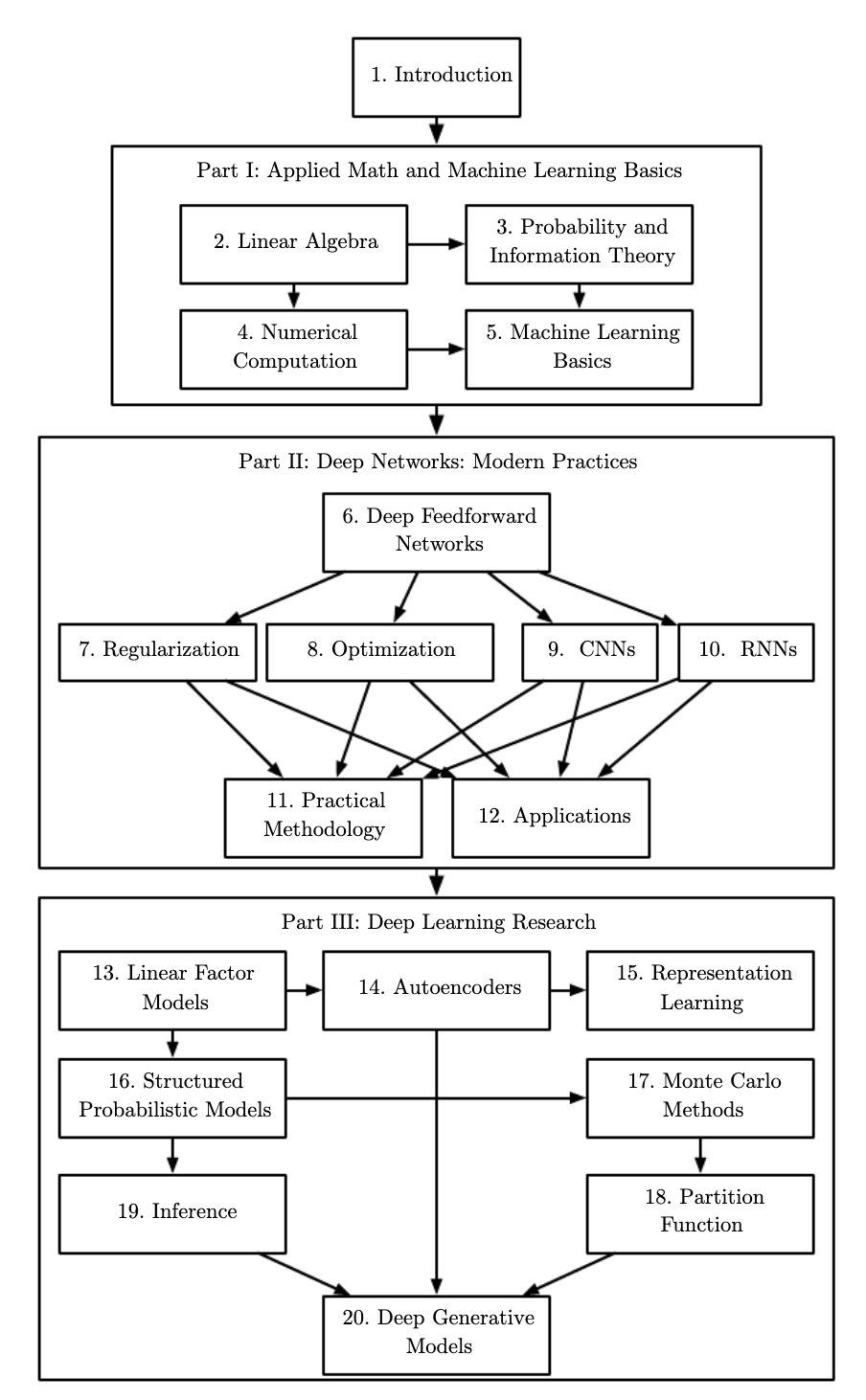
#concept-pamphlet #book Online textbook #todo compile alongisde other deep learning resources
summary
ch1 terms
- artificial intelligence
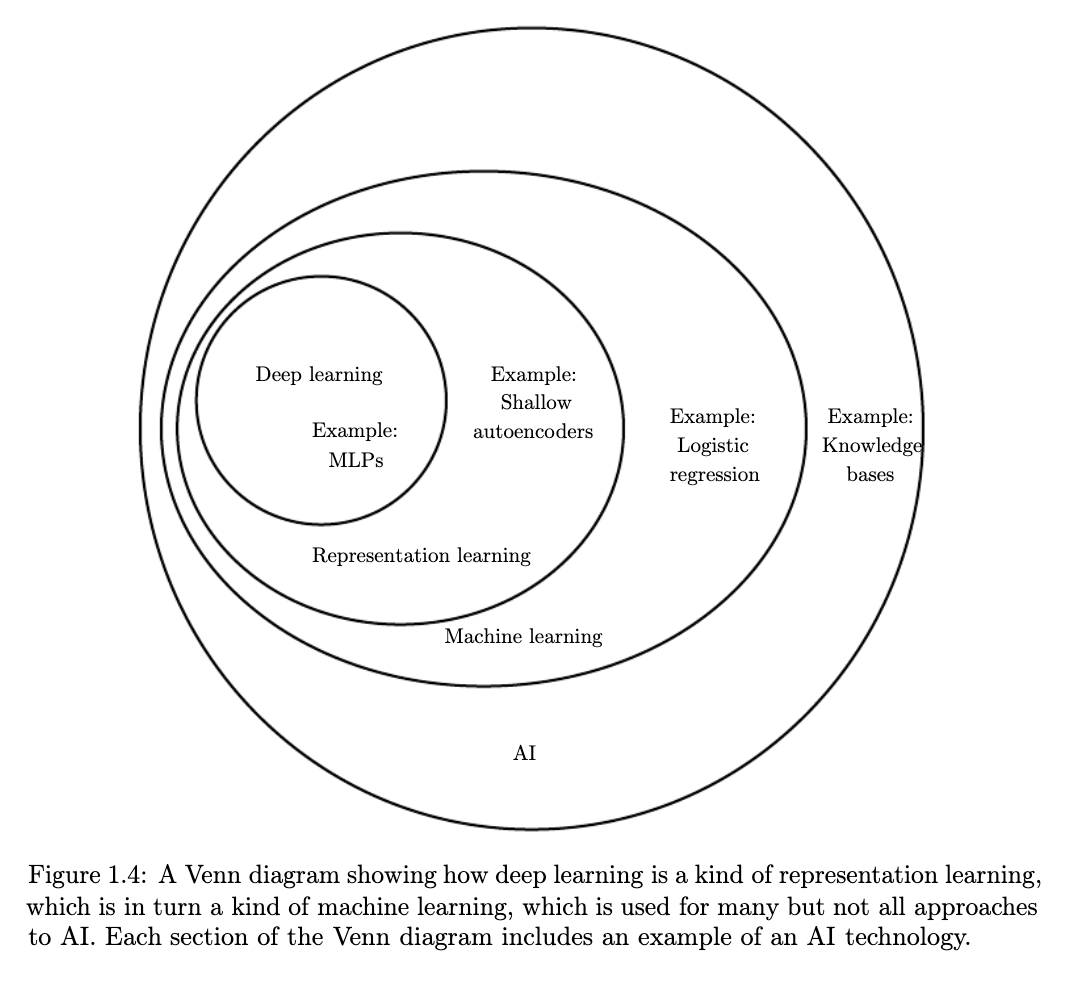
- deep learning
- knowledge base
- machine learning
- logistic regression
- naive Bayes
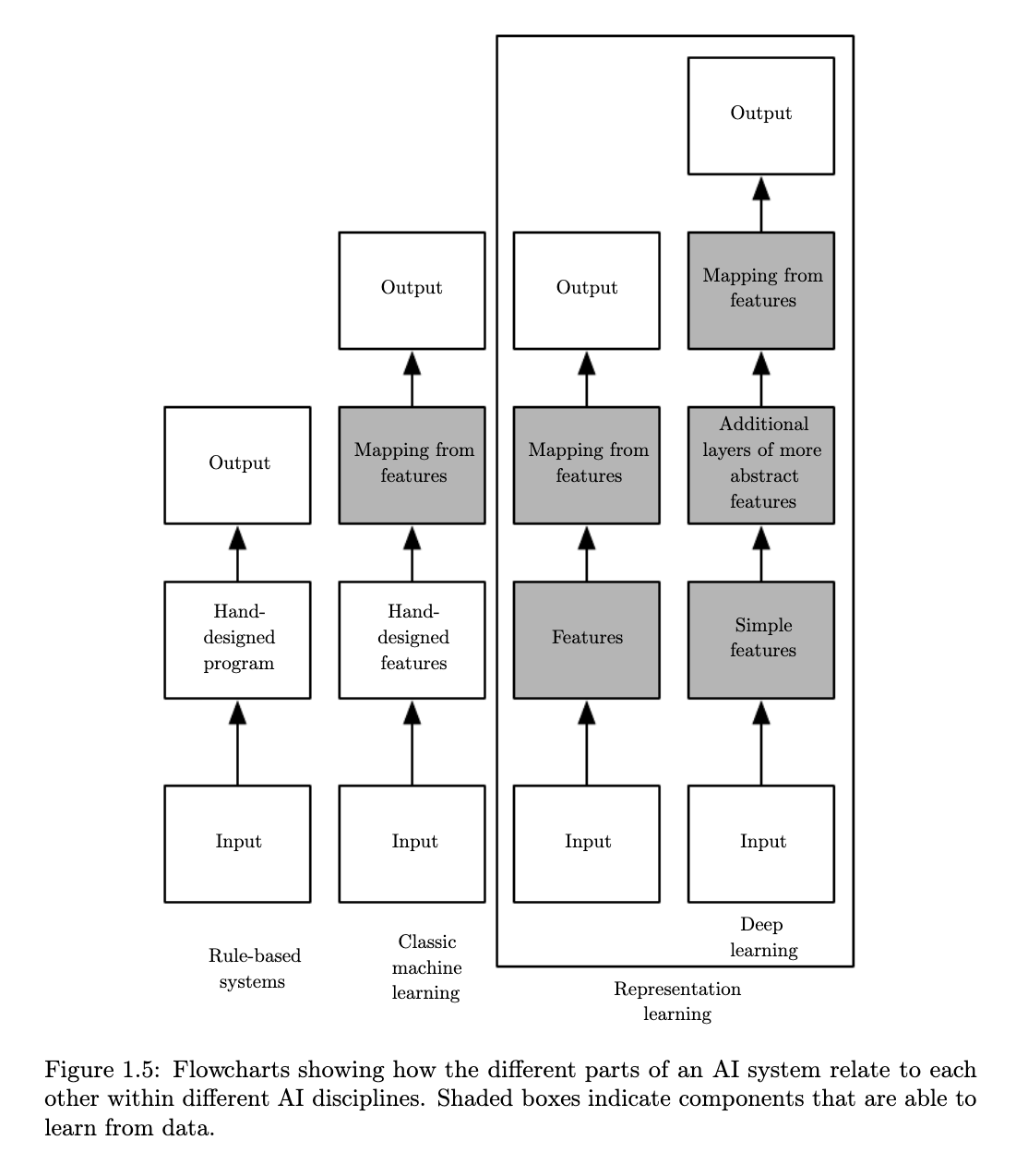
- representation
- feature
- representation learning
- autoencoder
- encoder
- decoder
- factors of variation
- multilayer perceptron (MLP): math function mapping some set of input values to output values. the function is formed by composing many simpler functions.
- visible layers
- hidden layers
ch2
- tensor
- transpose
- matrix product
- dot product
- identity matrix
- matrix inverse
- linear combination
- linear dependence, linear independence
- square matrix
- singular matrix
- norm
- euclidean norm
- max norm
- frobenius norm
- diagonal matrix
- symmetric matrix
- unit vector
- unit norm
- orthonormal
- orthogonal matrix
- eigen-decomposition
- eigenvector
- eigenvalue
- left eigenvector
- decompose
- positive definite, positive semidefinite, negativei definite, negativei semideinite
- singular value decomposition
- moore-penrose pseudoinverse
- principal components analysis
ch3
- 3 possible sources of uncertainty:
- inherent stochastiity: in system like subatomic particle movement. chaos
- incomplete observability: game show, outcome is deterministic but contestant doesn’t know that
- incomplete modeling: not all necessary data is used or weighted correctly. like time step discretization
terms. include specific equations where you can, pulled from reference material. include examples where helpful.
- degree of belief
- frequentist probability
- bayesian probability
- random variables
- may be discrete (finite) or continuous (real number)
- probability distribution
- probability mass function
- joint probability distribution
- normalized
- uniform distribution
- example of
- probability density function
- marginal probability distribution
- sum rule
- conditional probability
- chain rule / product rule
- independent
- conditionally independent
- expectation / expected value
- variance
- standard deviation
- covariance
- correlation
- covariance matrix
- bernoulli distribution
- multinoulli/ctaegorical distribution
- normal/Gaussian distribution
- precision
- central limit theorem
- multivariate normal distribution
- precision matrix
- exponential distribution
- laplace distribution
- generalized function
- empirical distribution
- empirical frequency
- mixture distribution
- latent variable
- Gaussian mixture
- prior probability
- posterior probability
- universal approximator
- logistic sigmoid
- softplus function
- logit
- positive part
- negative part
- bayes rule
- measure theory
- measure zero
- almost everywhere
- Jacobian matrix
- self-information
- nats
- bits / shannons
- shannon entropy
- differential entropy
- Kullback-Leibler divergence
- cross-entropy
- structured probabilistic model / graphical model
- directed models
- undirected models
- proportional
- description
ch4
- underflow
- overflow
- softmax function
- condition number
- objective / loss / error / cost function
- derivative
- gradient descent
- critical /stationary points
- local minimum
- local maximum
- saddle points
- global minimum
- partial derivatives
- gradient
- directional derivative
- gradient descent
- learning rate
- line search
- hill climbing
- Jacobian matrix
- curvature in relation to second derivatives
- Hessian matrix
- second derivative test
- Newton’s method
- first order optimization algorithms
- second order optimization algorithms
- lipschitz continuous
- convex optimization
- constrainted optimization
- Karush-Kuhn-Tucker approach
- generalized Lagrange function
- equality constraints and inequality constraints in the context of Langrangian
what is softmax?
?
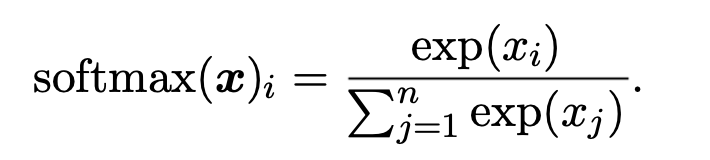
ch5
- classification
- classification with missing inputs
- regression
- transcription
- machine translation
- structured output
- anomaly detection
- synthesis and sampling
- imputation of missing values
- denoising
- density estimation / probability mass function estimation
- model accuracy: proportion of examples for which the model produces the correct output
- error rate: proportion of examples for which the model produces an incorrect output.
- unsupervised vs supervised learning
- reinforcement learning
- design matrix
- linear regression - include equatinos
- parameters in deep learning
- weights in deep learning
- bias in deep learning
- mean squared error
- normal equations - include examples
- generalization
- training error
- generalization error
- statstical learning theory
- data generating process, data generating distribution
- i.i.d. assumption: These assumptions are that the examples in each dataset are independent from each other, and that the train set and test set are identically distributed, drawn from the same probability distribution as each other. This assumption allows us to describe the data gen- erating process with a probability distribution over a single example.
- underfitting
- overfitting
- capacity in relation to model
- hypothesis space
- representational capacity
- effective capacity
- occam’s razor
- Vapnik-Chervonenkis dimension
- non-parametric models
- nearest neighbor regression
- Bayes error
- no free lunch theorem
- weight decay
- regularizer
- regularization
- hyperparameter
- capacity hyperparameter / degree of the polynomial
- validation set vs training set
- point estimator / statistic
- bias of an estimator
- asymptotically unbiased
- sample mean
- sample variance
- unbiased sample variance
- variance
- standard error
- mean squared error
- consistency
- almost sure convergence
- maximum likelihood estimation
- statistic efficiency
- parametric case
- frequentist statistics
- Bayesian statistics
- prior probability distribution
- bayesian linear regression
- posterior distribution
- maximum a posteriori estimation (MAP)
- logistic regression
- support vector machine
- kernel trick
- Gaussian kernel
- kernel machines / kernel methods
- support vectors
- decision tree
- principal components analysis (PCA)
- stochastic gradient descent
- minibatch
- curse of dimensionality
- local kernels
- manifold
- manifold learning
- manifold hypothesis
cards
spaced repetition